RDBMS와 JPA Entity에서 다대다의 표현
RDBMS에서 다대다(M:N) 관계를 표현하기 위해서는 관계테이블(Join Table)을 이용한다. 학생(Student) - 강좌(Course)의 다대다 관계를 테이블로는 아래와 같이 표기한다. course_like가 관계테이블이 된다.

POJO로 다대다 관계를 표현하는 것은 간단하게 관계를 맺는 클래스의 Collection 변수를 추가해주면 된다.
여기에 RDBMS에서 생성될 Model에 대한 추가정보를 애노테이션으로 설정해주면 아래 코드와 같이 작성할 수 있다.
@Entity
class Student {
@Id
Long id;
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(
name = "course_like",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "student_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "course_id"))
Set<Course> likedCourses;
// additional properties
// standard constructors, getters, and setters
}
@Entity
class Course {
@Id
Long id;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "likedCourses")
Set<Student> likes;
// additional properties
// standard constructors, getters, and setters
}
- @ManyToMany : 다대다 관계를 표현한다.
- @JoinTable : RDBMS에 생성될 관계테이블에 대해 정의한다. 관계를 구성해주는 쪽을 Owner로 하며 예제에서는 Student가 Owner이다.
- @JoinColumn : 관계테이블의 FK에 대한 설정이다. Student의 FK를 student_id 컬럼명, Course의 FK를 course_id 컬럼명으로 생성한다.
- @ManyToMany(mappedBy = “likedCourses”) : Owner와 관계를 맺는 Target 에서 Owner의 어떤 컬럼과 맵핑되는지 정의한다.
위 예제는 Student, Course 엔티티를 직접적으로 연결하고 있다. 즉 관계 테이블이 엔티티로 코드에 존재하지 않는다. 관계테이블은 FK로만 구성되어 있으며 별도의 프로퍼티를 가질 수 없다.
Composite Key를 사용하는 ManyToMany
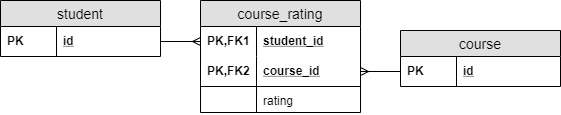
학생이 강좌를 평가하는 것을 모델링한다면 RDBMS 에서는 다음같이 표현한다. 여기서 rating 프로퍼티를 위 코드처럼 엔티티를 직접 연결해서는 표현할 수 없다.
그러므로 관계테이블(course_rating)을 엔티티로 승격시켜 코드로 작성하고 여기에 rating 프로퍼티를 추가한다. Key가 2개 이상이므로 가독성을 위해 복합키(Composite Key)로 작성해본다.
@Embeddable
class CourseRatingKey implements Serializable {
@Column(name = "student_id")
Long studentId;
@Column(name = "course_id")
Long courseId;
// standard constructors, getters, and setters
// hashcode and equals implementation
}
- @Embeddable : 다른 엔티티에 프로퍼티로 추가할 수 있다는 표시
- 복합키는 java.io.Serializable 를 구현해야 한다.
- 복합키는 hashcode(), equals() 를 구현해야 한다.
@Entity
class CourseRating {
@EmbeddedId
CourseRatingKey id;
@ManyToOne
@MapsId("student_id")
@JoinColumn(name = "student_id")
Student student;
@ManyToOne
@MapsId("course_id")
@JoinColumn(name = "course_id")
Course course;
int rating;
// standard constructors, getters, and setters
}
- @EmbeddedId : @Embeddable이 마킹된 복합키 클래스를 가져온다.
- @ManyToOne : 관계테이블은 관계를 구성하는 두 개의 테이블과 각각 ManyToOne 관계를 맺는다.
- @MapsId : 복합키의 student_id와 student 프로퍼티를 연결한다.
class Student {
// ...
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "student")
Set<CourseRating> ratings;
// ...
}
class Course {
// ...
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "course")
Set<CourseRating> ratings;
// ...
}
- @OneToMany(mappedBy = “student”) : Target 클래스에서 mappedBy 속성으로 Owner의 student 프로퍼티와 연결한다.
복합키를 사용하지 않고 별도의 ID를 갖는 ManyToMany Entity
학생이 강좌를 수강하고 성적을 받는 것을 생각해본다. 학생은 같은 강좌를 여러번 수강할 수 있고 이에따라 성적도 복수개가 저장되어야 한다. 위 예제처럼 FK의 조합으로는 여러번 수강하는 것에대한 표현이 불가능하니 별도의 ID를 두고 관계를 표현한다.

@Entity
class CourseRegistration {
@Id
Long id;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "student_id")
Student student;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "course_id")
Course course;
LocalDateTime registeredAt;
int grade;
// additional properties
// standard constructors, getters, and setters
}
class Student {
// ...
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "student")
Set<CourseRegistration> registrations;
// ...
}
class Course {
// ...
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "courses")
Set<CourseRegistration> registrations;
// ...
}
